The code excerpt below is from EmbeddedPersonServiceClientTest, and is run before
any of the tests are run to initialize Jetty. Even though this is a unit test, this would be the
same code that would be used to start a standalone Spring application. It could contain
an executor pool, db connection pool, timer processes, etc.
The main application context is initialized, and then the Jetty Server bean is retrieved from it.
Then the ServletContext from the Spring Web Services webapp is retrieved.
An intermediary web application context is created between the main application context and the
Spring Web Services context. The intermediary web context is then set as an attribute on the ServletContext
under the constant WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, which indicates
it should be used as the parent context for the web application. Then the Jetty server is ready to be started.
Example 1. EmbeddedPersonServiceClientTest
AbstractApplicationContext ctx =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("/org/springbyexample/ws/embedded/embedded-jetty-context.xml"); 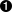 ctx.registerShutdownHook();
Server server = (Server) ctx.getBean("jettyServer");
ctx.registerShutdownHook();
Server server = (Server) ctx.getBean("jettyServer");  ServletContext servletContext = null;
for (Handler handler : server.getHandlers()) {
if (handler instanceof Context) {
Context context = (Context) handler;
servletContext = context.getServletContext();
ServletContext servletContext = null;
for (Handler handler : server.getHandlers()) {
if (handler instanceof Context) {
Context context = (Context) handler;
servletContext = context.getServletContext(); }
}
XmlWebApplicationContext wctx = new XmlWebApplicationContext();
}
}
XmlWebApplicationContext wctx = new XmlWebApplicationContext();  wctx.setParent(ctx);
wctx.setConfigLocation("");
wctx.setServletContext(servletContext);
wctx.refresh();
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, wctx);
wctx.setParent(ctx);
wctx.setConfigLocation("");
wctx.setServletContext(servletContext);
wctx.refresh();
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, wctx);  server.start();
server.start(); 